
As for the goethite, the PZC (10.9 ± 0.05) was slightly higher than the PZNC (9.0-9.4). The PZC of kaolinite (3.01 ± 0.03) was similar to the PZNC (2.9-3.4) and fell within the range of values reported in the literature (2.7-4.1). Determination of the surface potential and isoelectric point of wafers with a zeta potential analyzer. Both the ion adsorption and the zeta potential methods failed to give points of zero charge for these substrates. We used the SARS-CoV-2 proteins currently available on the market, namely the RBD with His- and Fc-tag, the S1 subunit with His-tag, and the S1/S2 subunits with His-tag. The isoelectric point of mAb A is above pH 9, and the isoelectric point of mAb B is below pH 8 (relative difference between them is 1.5 units), which again puts both mAbs on the opposite sides of. Results obtained from the salt addition method in 0.05 M NaNO 3 were the following: 4.72 ± 0.06 (maple sawdust), 9.50 ± 0.07 (wood ash), 3.42 ± 0.03 (peat moss), 7.68 ± 0.01 (green compost), and 6.06 ± 0.11 (brown algae). Since the isoelectric point of proteins is an important property, we sought to determine it using the Maurice (imaged) CIEF system from ProteinSimple, a Bio-Techne brand. Urea is often used in CIEF to improve protein solubility near the isoelectric point, however, urea concentration can affect resolution of charge variant species and the apparent pI the manufacturer recommended concentration for this CIEF kit is 3 mol/L.

Knowing the pI can be important for predicting e.g. Natural kaolinite and synthetic goethite were also tested with both the salt addition and the ion adsorption methods in order to validate experimental protocols. The isoelectric point (pI) of a molecule is the pH at which the molecule carries no net charge. The isoelectric point is the pH at which a particular molecule is electrically neutral due to the equilibrium of positive and negative charges. Three methods were used: (1) the salt addition method, measuring the PZC (2) the zeta potential method, measuring the isoelectric point (IEP) (3) the ion adsorption method, measuring the point of zero net charge (PZNC). The net charge on the molecule is affected by the pH of. The PZC provides important information about metal sorption mechanisms. The isoelectric point (pI) is the pH at which a particular molecule carries no net electrical charge. Note that the colors in the display are only a convenient reference, since these amino acids are colorless.Īt pH 6.00 alanine and isoleucine exist on average as neutral zwitterionic molecules, and are not influenced by the electric field.This study evaluates different methods to determine points of zero charge (PZCs) on five organic materials, namely maple sawdust, wood ash, peat moss, compost, and brown algae, used for the passive treatment of contaminated neutral drainage effluents. Through protonation and deprotonation reactions, as a result of the amphoteric nature of water, positive or negative charges can be generated on the surface.

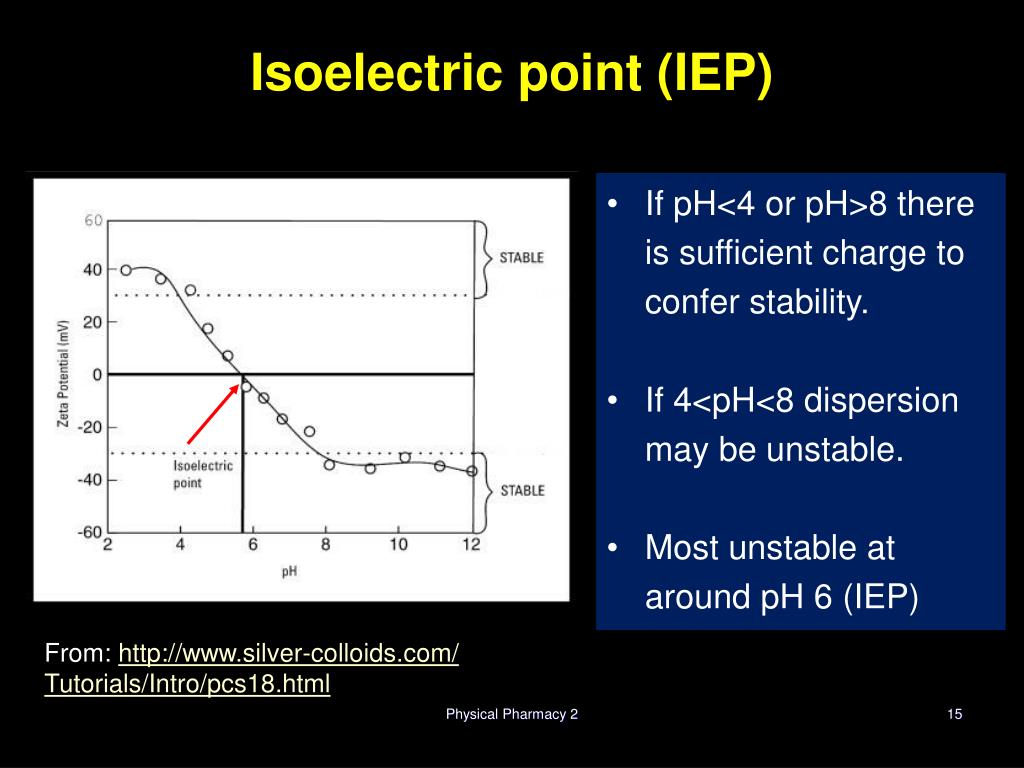
To see the result of this experiment, click on the illustration. The isoelectric point (IEP) and the point of zero charge (PZC) reflect the response of a surface to an electrolyte, typically water. \): In the example shown here, four different amino acids are examined simultaneously in a pH 6.00 buffered medium. The present paper deals with the electrokinetic characterization of sepiolite. The isoelectric point (pI) of a protein is a key characteristic that influences its overall electrostatic behaviour.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
